Geographic Information Systems
Program Guidance Documents
- GIS Management Plan
- GIS Quality Assurance Project Plan (EPA)
- Standard Operating Procedures
Environmental Studies and Research Institute (ESRI) software
- Dedicated server for repository for all raw geospatial data
- ArcGIS for server enterprise concurrent license as platform to network servers
- ArcGIS server manager – intra-departmental connection for functionality
- ArcGIS Pro 3.4.1
Geospatial Data Inventory
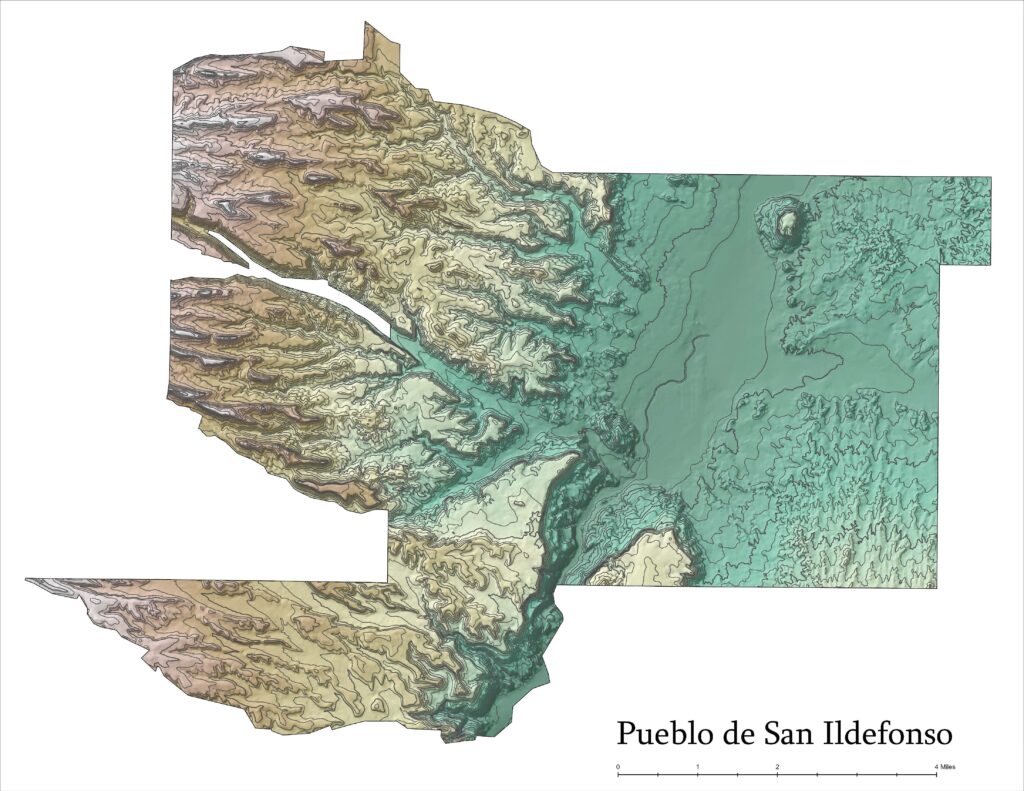
- Raster, Vector, Maps, Aerial Imagery, LIDAR , Surface Terrain
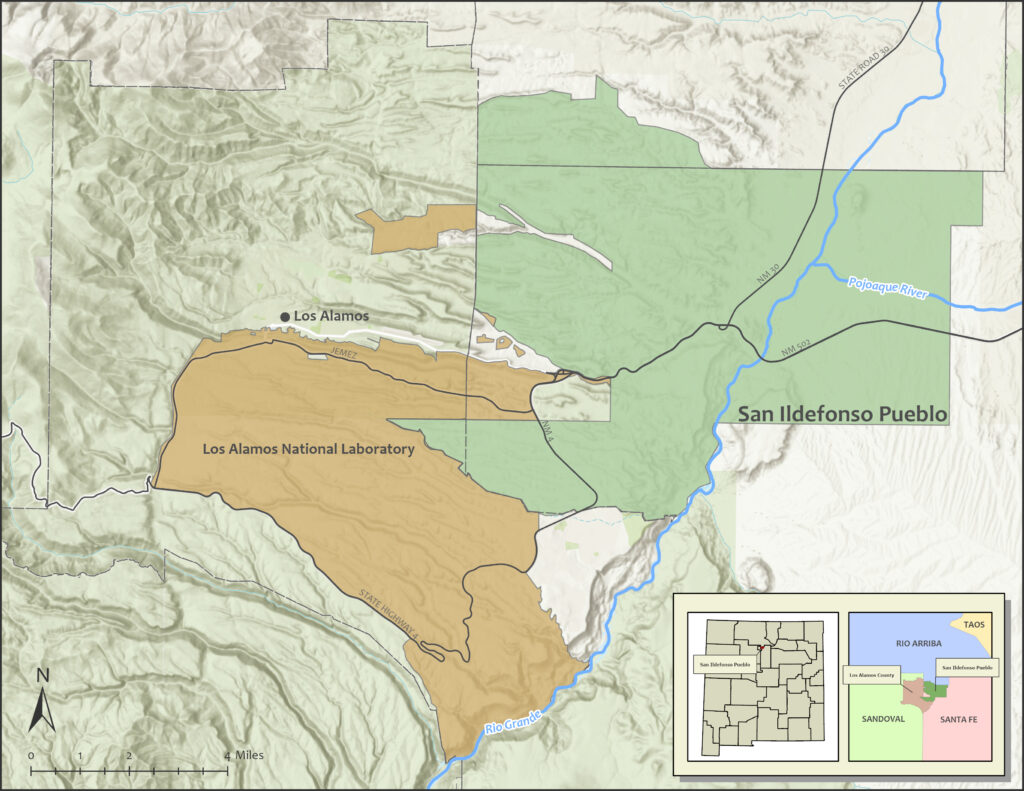
- Data Layer Collection: BIA, County of Santa Fe, USGS, NMED, LANL
GIS Map Services
Layer Library
- Permission based user friendly data layers
- Linked with environmental tabular database
- Remains “Dynamic”
Map Catalog
- Open file server
- Production maps
- Remains “Static”
Environmental Monitoring and Map Production
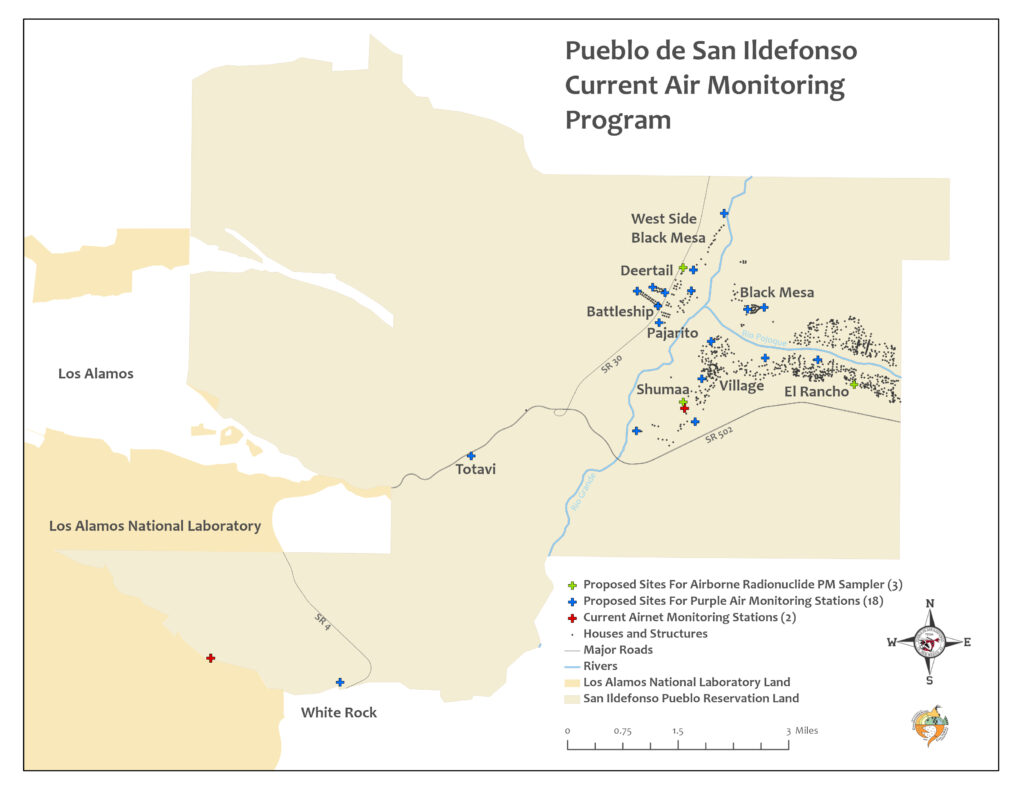
- Provide layers and geospatial data for Environmental mapping tools
- Sample event planning
- Identify landmarks, hydrology, significant structures and restricted areas
- Historical studies
About GIS
GIS is a system of hardware and software used for storage, retrieval, mapping, and analysis of geographic data.
- Layers are files that store symbology and display information for a given vector or raster data set.
- Vectors are data models based on a coordinate system used to represent linear geographic features.
- Rasters are data models composed of a grid of cells which represent data with a spatial component.
- Attributes are information (text or numeric) about a geographic feature generally stored in a table that is linked to the feature which might include names, distances, depth, etc.
- Features are objects in a landscape or on a map.
- Geospatial data – Geographic data is the data or information that identifies the geographic location of features and boundaries on Earth.
- DECP’s GIS department utilizes the Bureau of Indian Affairs’ Branch of Geospatial Support to acquire the most contemporary GIS software available within ESRI’s suite of products.
